What are polyatomic ions?
Ions are formed when neutral atoms gain or lose electrons. Similarly, a polyatomic ion is formed when a neutral molecule gains or loses electrons.
- A polyatomic ion is a charged group of atoms covalently bonded together.
- Majority of the polyatomic ions are anions, meaning they are negatively charged.
- Ammonium is the only positively charged polyatomic ion that does not have an oxygen atom.
- And many polyatomic ions are combined with one or more oxygen atoms, and their names end in either “ite” or “ate”.
A polyatomic ion compound
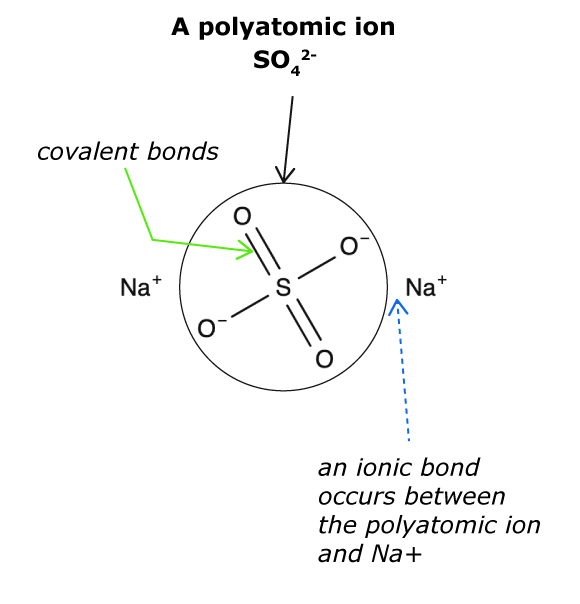
Polyatomic ions are usually anions (negatively charged), so they would be attracted to cations (positively charged).
A polyatomic ion can be attracted to an oppositely charged element, or an oppositely charged polyatomic ion.
- NH₄⁺ attracted to F⁻
- NH₄⁺ attracted to SO₄²⁻
In all cases, the charges must always be balanced in a compound.
Balance the charges
| Cation (Na⁺) | Anion (SO₄²⁻) |
|---|---|
| + | 2- |
| + |
Formula: Na₂SO₄
| Cation (NH₄⁺) | Anion (SO₄²⁻) |
|---|---|
| + | 2- |
| + |
Formula: (NH₄)₂SO₄
Make sure you always put brackets around the polyatomic ion if there are more that one of them in the formula
Naming compounds containing polyatomic ions
The convention for naming polyatomic ion compounds is the same as for the ionic compounds.
Name the cation first before the anion.
| Name | Cation | Anion | Formula |
|---|---|---|---|
| Magnesium carbonate | Mg²⁺ | CO₃²⁻ | MgCO₃ |
| Ammonium nitrate | NH₄⁺ | NO₃⁻ | NH₄NO₃ |
| Calcium carbonate | Ca²⁺ | CO₃²⁻ | CaCO₃ |
Transition elements
If transition elements are present, use Roman numerals to indicate the charges of the cation.
| Name | Cation | Anion | Formula |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chromium(II) phosphate | Cr²⁺ | PO₄³⁻ | Cr₃(PO₄)₂ |
| Chromium(III) phosphate | Cr³⁺ | PO₄³⁻ | CrPO₄ |
The diagrams below show how the charges are balanced for the compounds.
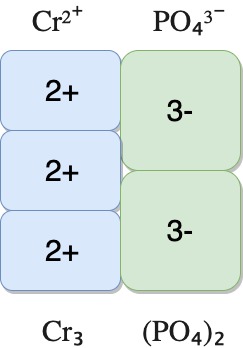
chromium(II) phosphate
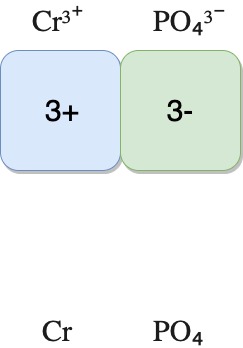
chromium(III) phosphate
Acids
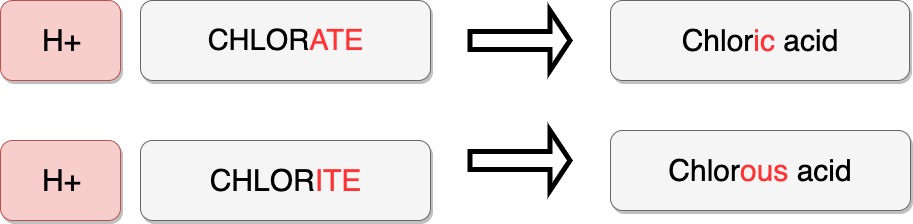
Acids are compounds in which the “cation” is H+ .
Acids are named based on their anion.
A polyatomic ion with suffix ending in “-ate” is changed to the suffix “ic” as an acid.
A polyatomic ion with suffix ending in “-ite” is changed to the suffix “ous” as an acid.
Memorizing polyatomic ions names
How to memorize the names and chemical formulas of polyatomic ions such as carbonate (CO3–), phosphate (PO43–), nitrate (NO3–) and sulfate (SO42–)? If you notice the pattern, these names end in either “ite” or “ate”. These species contain oxygen atoms, and their names are based on the number of oxygen atoms in the ion. You can find the charges on the periodic table, as we will discuss on the next page.
How to memorize the names of polyatomic ions and their charges >>
Concept check
Concept check
Concept check
Memorizing the names of polyatomic ions
Memorizing names of polyatomic ions >>

